The Fed’s Rate Cuts: Unintended Consequences for the Housing Market
As the Federal Reserve prepares to potentially lower interest rates, the ripple effects on various sectors of the economy are under intense scrutiny. One area of particular interest is the housing market, which has been struggling with high prices and low inventory despite broader economic changes. The Fed’s anticipated rate cuts could potentially provide relief, but they may also lead to unintended consequences that could complicate the housing market’s dynamics.
The Housing Market’s Persistent Challenges
To fully grasp the impact of potential rate cuts, it’s important to understand the current challenges facing the housing market. The imbalance between supply and demand remains one of the most pressing issues. This imbalance means that there are more people looking to buy homes than there are homes available for sale. This issue was evident even before the COVID-19 pandemic, but it has been exacerbated by the economic disruptions caused by the pandemic.
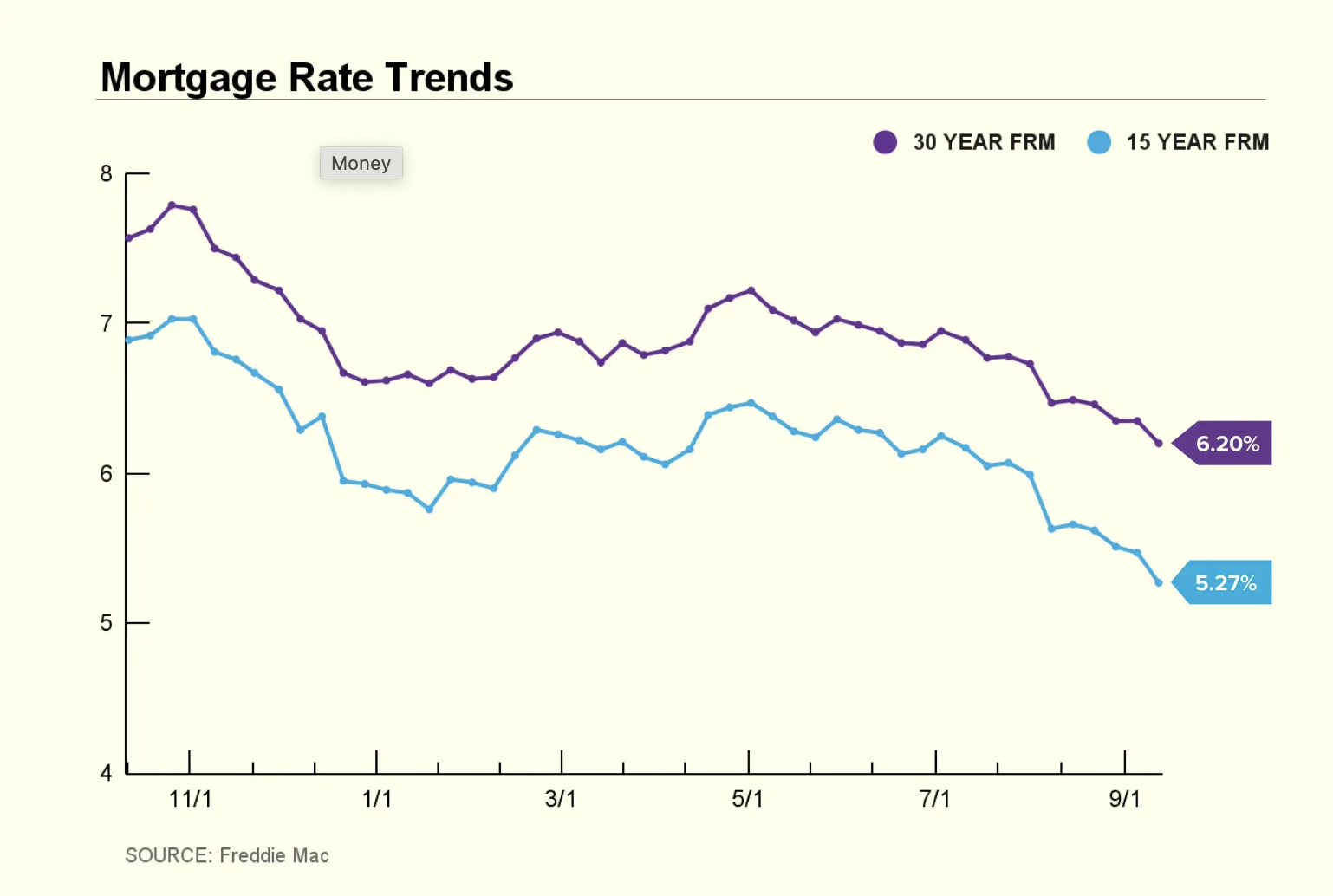
Prior to the pandemic, mortgage rates were relatively stable, and the housing market was characterized by moderate growth in home prices. However, the onset of the pandemic led to a dramatic shift. Mortgage rates fell to historic lows, driven by the Federal Reserve’s aggressive monetary policy aimed at supporting the economy during a period of unprecedented uncertainty. This drop in rates spurred a surge in homebuying activity, as low borrowing costs made homeownership more accessible for many buyers.
However, as the pandemic progressed, the economic environment changed. The Fed’s initial rate cuts were followed by a period of economic recovery, during which inflation began to rise. In response, the Fed increased interest rates to combat inflation, leading to a sharp rise in mortgage rates. This shift created a new set of challenges for the housing market, with rising borrowing costs putting additional pressure on home prices and limiting affordability for many prospective buyers.
The Fed’s Role in Shaping Housing Market Dynamics
The Federal Reserve wields significant influence over the economy through its control of interest rates. By adjusting the federal funds rate, the Fed can impact borrowing costs across various sectors, including the housing market. When the Fed raises rates, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can slow down economic activity. Conversely, when the Fed lowers rates, borrowing costs decrease, which can stimulate economic activity and encourage spending and investment.
In recent months, inflation has shown signs of moderating, prompting speculation that the Fed may consider lowering interest rates. Lowering rates could potentially have a positive effect on the housing market by making mortgage loans more affordable. This could lead to increased homebuying activity and potentially ease some of the affordability pressures that have been prevalent in the market.
However, the potential impact of rate cuts on the housing market is not straightforward. Several factors will influence how effective these cuts will be in improving home affordability and addressing the underlying issues facing the market.
The Impact of Rate Cuts on Home Affordability
One of the primary goals of lowering interest rates is to improve home affordability. Lower mortgage rates can reduce monthly payments, making homeownership more accessible for potential buyers. For instance, if the Fed were to implement a significant rate cut, it could lead to lower mortgage rates, which would reduce the cost of borrowing and potentially increase buyers’ purchasing power.
However, the effectiveness of rate cuts in improving affordability will depend on the overall supply and demand dynamics in the housing market. Even if mortgage rates decrease, the limited supply of available homes could continue to put upward pressure on prices. If demand for homes increases due to lower rates, but the supply of homes remains constrained, this could lead to higher home prices, which may offset the benefits of lower borrowing costs.
Additionally, the psychological impact of lower rates cannot be underestimated. A reduction in mortgage rates can create a sense of urgency among buyers, leading to increased competition for available homes. This heightened demand could further drive up prices, making it even more challenging for prospective buyers to afford a home.
Supply Constraints and the Fed’s Rate Cuts
While rate cuts can influence borrowing costs, they do not directly address the issue of housing supply. The housing market has been grappling with a shortage of available homes, which has been a major contributor to high home prices. The “lock-in” effect is one of the key factors contributing to this supply constraint.
The “lock-in” effect refers to the phenomenon where homeowners with low-interest mortgages are reluctant to sell their homes and move, especially if they would face higher borrowing costs on a new mortgage. This reluctance to sell limits the number of homes available for prospective buyers, exacerbating the supply shortage and contributing to higher home prices.
The Fed’s rate cuts may alleviate some of the borrowing cost pressures, but they may not be sufficient to overcome the supply constraints in the housing market. Even if rate cuts lead to a temporary increase in housing inventory, this may be offset by ongoing challenges in new home construction. High construction costs, regulatory barriers, and other factors have contributed to a slowdown in new home building, which has further constrained the supply of available homes.
The Psychological and Market Dynamics
The psychological impact of Fed rate cuts on the housing market is a critical consideration. A reduction in mortgage rates can create a sense of optimism and urgency among potential buyers. Lower rates may encourage more people to enter the market, potentially leading to a surge in homebuying activity.
However, this psychological boost may not be sustained if the underlying supply constraints are not addressed. Prospective buyers may become excited about the prospect of lower borrowing costs, but if they find that prices remain high due to limited inventory, their enthusiasm could quickly diminish. This could lead to a scenario where increased demand driven by lower rates does not translate into improved affordability but rather reinforces existing market pressures.
The Fed’s actions could also influence investor behavior in the housing market. Lower rates may attract more investors looking to capitalize on the potential for higher returns in real estate. This increased investment activity could further drive up home prices, making it even more challenging for first-time homebuyers and other prospective buyers to secure affordable homes.
The Risk of a Demand Surge
One of the potential unintended consequences of Fed rate cuts is a surge in demand that exceeds the housing market’s capacity to respond. As mortgage rates decrease, more buyers may be encouraged to enter the market, potentially leading to increased competition for available homes. This surge in demand could exacerbate existing supply shortages and drive prices even higher.
This phenomenon has been observed in previous economic cycles. When interest rates drop, it often leads to a temporary boost in housing market activity. However, if supply constraints are not addressed, this increased demand can lead to higher home prices, making the market even less affordable for many buyers.
Greg McBride, chief financial analyst at Bankrate, cautions that a further drop in mortgage rates could lead to a surge in demand that makes it even more difficult for buyers to find affordable homes. While lower rates may provide some relief, they could also create new challenges if not accompanied by improvements in housing supply.
Long-Term Implications and Policy Considerations
The long-term implications of Fed rate cuts for the housing market will depend on several factors, including the broader economic environment and housing policy decisions. While rate cuts can provide short-term relief, they are not a panacea for the complex issues facing the housing market.
To address the affordability crisis and ensure a more balanced housing market, policymakers and stakeholders will need to consider a comprehensive approach that includes both monetary policy and structural reforms. Key areas for consideration include:
- Increasing Housing Supply: Efforts to boost new home construction and reduce barriers to building can help alleviate supply constraints. This may involve reforms to zoning laws, streamlining permitting processes, and incentivizing developers to build more affordable housing. Addressing these supply issues is crucial to ensuring that the benefits of lower mortgage rates translate into improved affordability for buyers.
- Addressing the Lock-In Effect: Policymakers might consider measures to mitigate the lock-in effect, such as offering refinancing options or incentives for existing homeowners to sell and move. By addressing this issue, it may be possible to increase the number of homes available for sale and alleviate some of the supply constraints in the market.
- Supporting First-Time Buyers: Targeted assistance for first-time homebuyers, such as down payment assistance programs and affordable mortgage options, can help improve access to homeownership. Providing support for these buyers can help ensure that they are able to take advantage of lower mortgage rates and achieve their homeownership goals.
- Monitoring Market Conditions: Ongoing monitoring of housing market trends and adjusting monetary policy accordingly will be crucial to ensuring that rate cuts have the desired effects without exacerbating existing issues. By staying attuned to market conditions, the Fed can make informed decisions that support a more balanced and accessible housing market.
- Promoting Financial Literacy: Educating potential homebuyers about the impacts of interest rates, home prices, and market conditions can empower them to make informed decisions. Financial literacy programs can help buyers navigate the complexities of the housing market and make choices that align with their long-term financial goals.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve’s anticipated rate cuts are poised to have a significant impact on the housing market in 2024. While these cuts could lower borrowing costs and improve home affordability for some buyers, they also carry the risk of exacerbating existing challenges. The interplay between lower rates, supply constraints, and market dynamics will shape the ultimate effects of these policy changes.
Addressing the housing market’s fundamental issues requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond monetary policy. By focusing on increasing housing supply, mitigating the lock-in effect, supporting first-time buyers, and monitoring market conditions, policymakers can work towards a more balanced and accessible housing
Other Post
Israel-Lebanon Tensions: Hezbollah Vows Retaliation After Deadly Pager Explosions Killing 9